Human spine garetboston
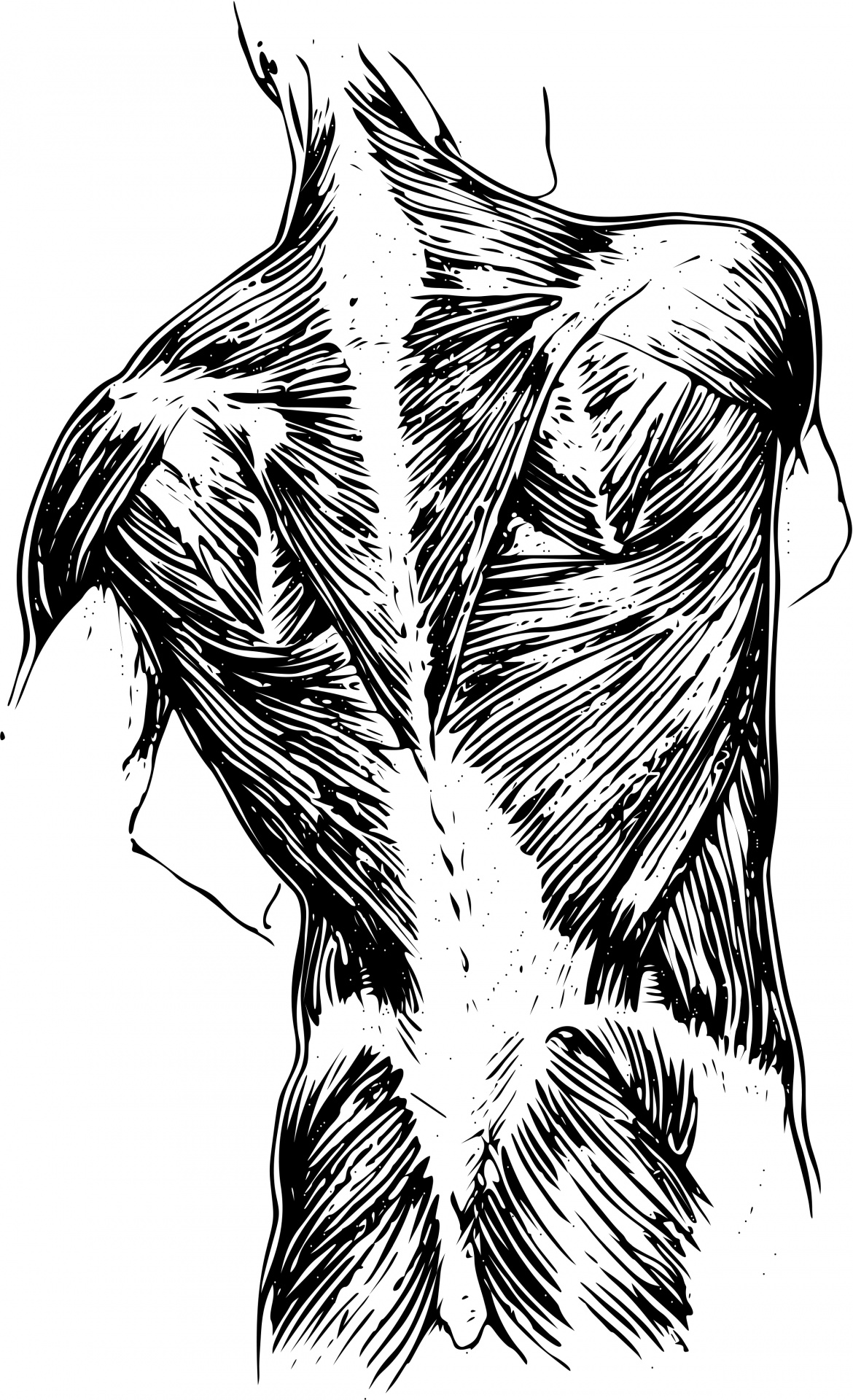
Anatomy of Back Muscles Your back consists of three distinct layers of muscles, namely the superficial layer, the intermediate layer, and the deep layer. These layers of back muscles help to mobilize and stabilize your trunk during your day to day activities.
Human Spine Photograph by Andrzej Wojcicki/science Photo Library Pixels
The muscles of the back can be arranged into 3 categories based on their location: superficial back muscles, intermediate back muscles and intrinsic back muscles.The intrinsic muscles are named as such because their embryological development begins in the back, oppose to the superficial and intermediate back muscles which develop elsewhere and are therefore classed as extrinsic muscles.

64328865 3d illustration of spine part of human skeleton
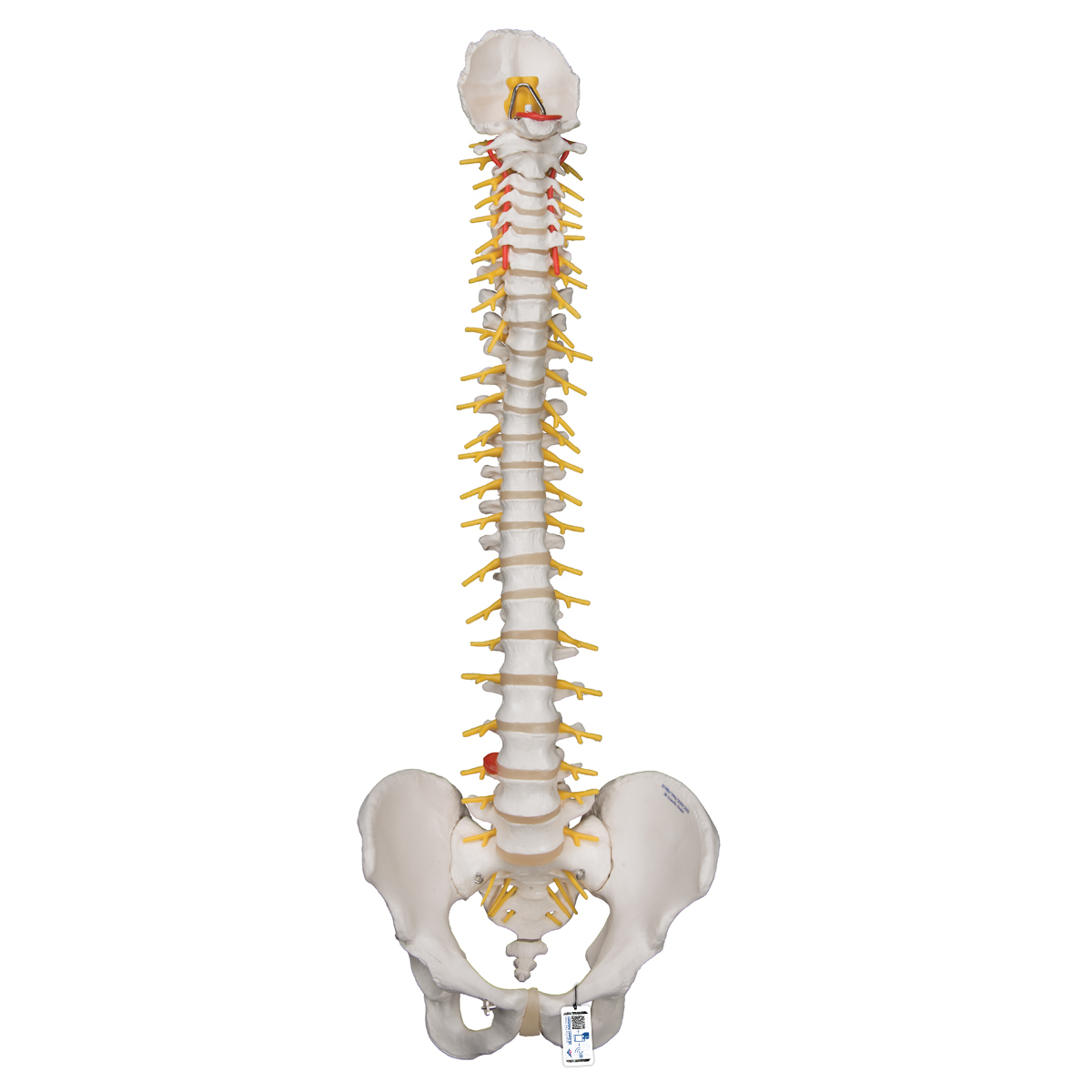
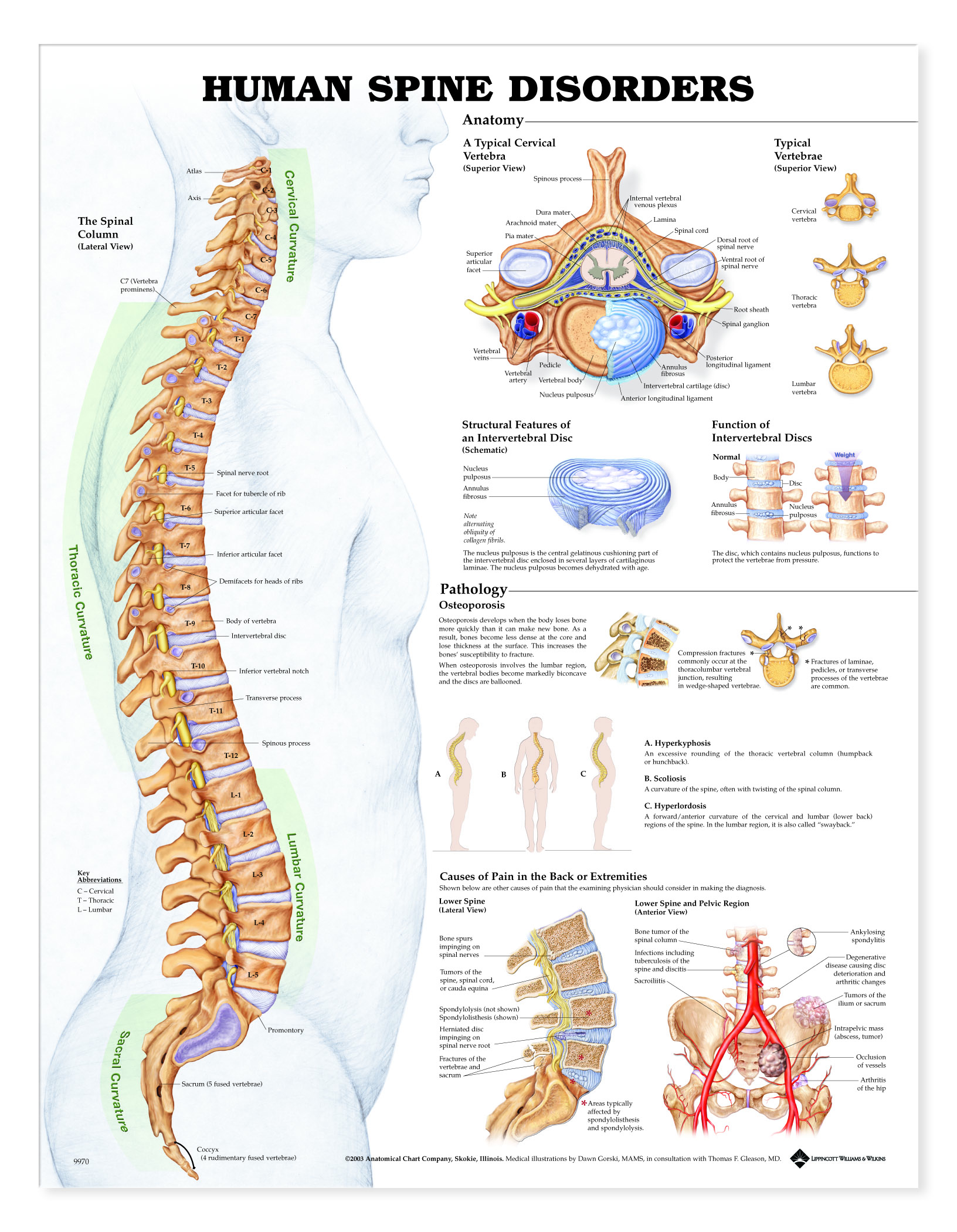
Vertebrae Numbering order of the vertebrae of the human spinal column The vertebrae in the human vertebral column is divided into different regions, which correspond to the curves of the vertebral column. The articulating vertebrae are named according to their region of the spine.

bodyman Full back muscles
Human body Skeletal System Spine Spine The spinal cord begins at the base of the brain and extends into the pelvis. Many of the nerves of the peripheral nervous system, or PNS, branch out.

Structure Of Back Bones
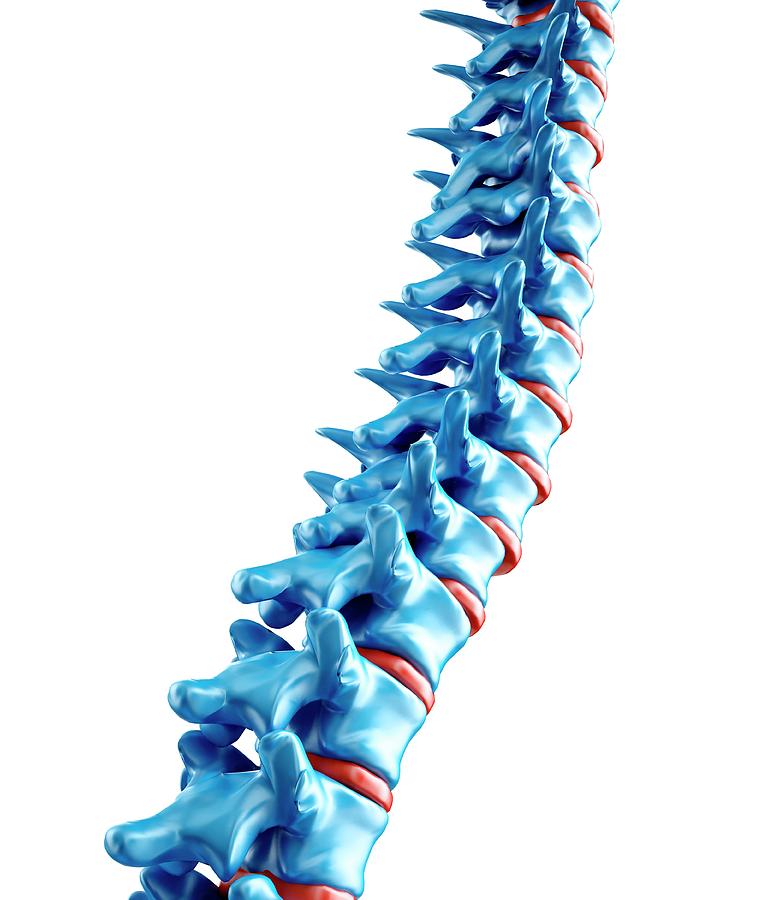
The bones of the back, together, make up the vertebral column.The vertebral column is made up of 5 sections: the cervical vertebrae, the thoracic vertebrae, the lumbar vertebrae, the sacrum and the coccyx.These sections total 33 vertebrae which function together to aid locomotion and posture as well as providing support and protection. Whilst each section of the vertebral column consists of.

Human back anatomy, illustration Stock Image F011/5857 Science
Vertebrae, along with intervertebral discs, compose the vertebral column or spine. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the coccyx and includes the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions. The spine has several significant roles in the body, including protection of the spinal cord and branching spinal nerves, support for the thorax and abdomen, and enabling flexibility and.
Human Back Muscles Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
The human back consists of a complex structure of muscles, ligaments, tendons, disks, and bones that work together to support the body and enable movement. The segments of the spine are cushioned.
Lower back pain 360 Physiotherapy Norwich
The back supports the body's weight and allows for flexible movement while protecting vital organs and nerve structures. It comprises the spine, nerves, and other crucial elements. Problems.
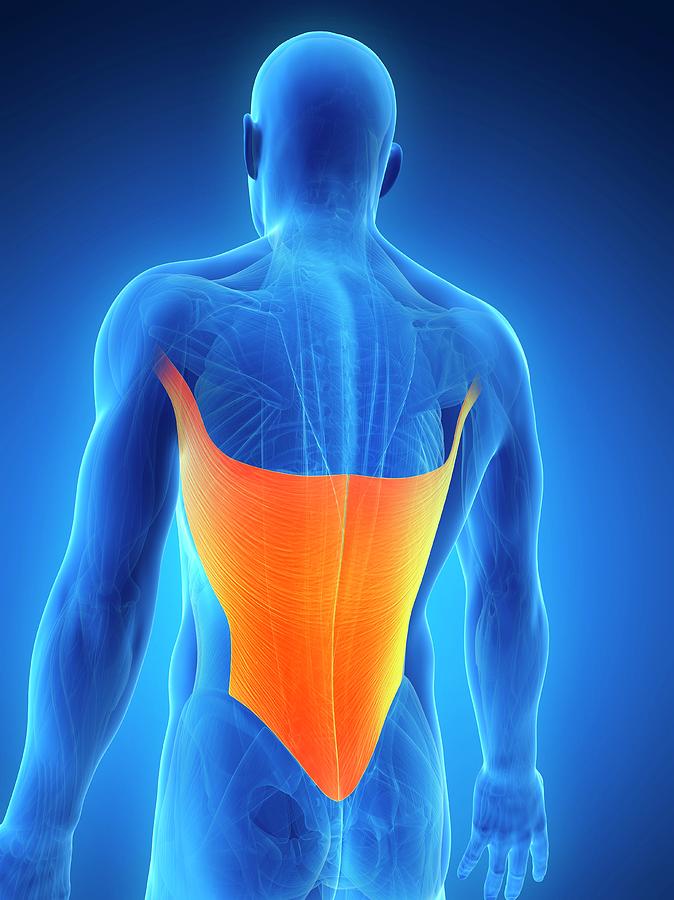
Human Back Muscles Photograph by Sebastian Kaulitzki
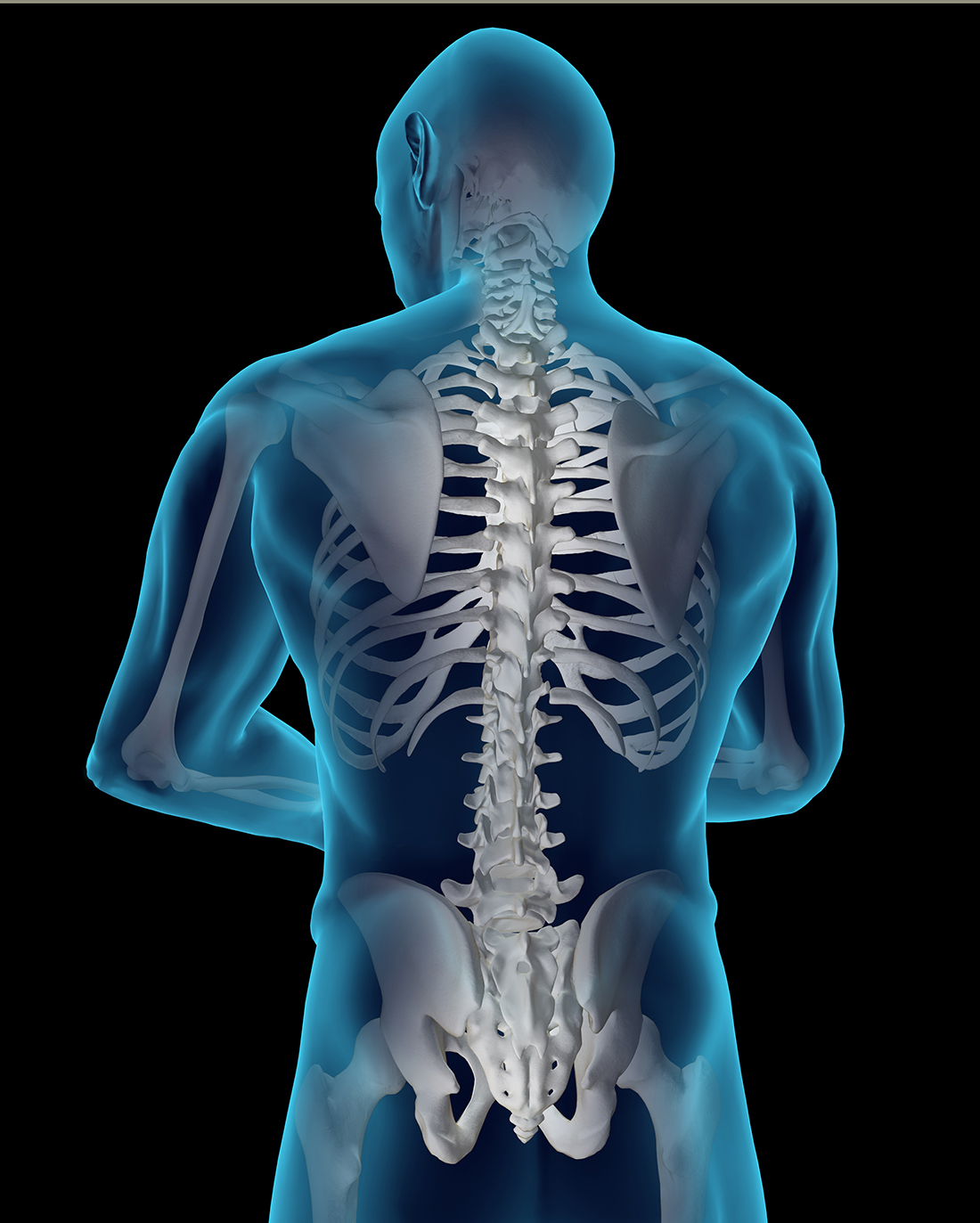
Back anatomy The back is the body region between the neck and the gluteal regions. It comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments of back muscles; extrinsic and intrinsic. The back functions are many, such as to house and protect the spinal cord, hold the body and head upright, and adjust the movements of the upper and lower limbs.
Benefits of a Healthy Spine Keep Healthy Living
The vertebral column supports the body's physical structure and nervous system, enabling movement and sensation. Pathology of the spine can lead to debilitating outcomes on quality of life. The vertebral column (spine) defines the animal subphylum Vertebra, or vertebrates, of the phylum Chordata. In humans, it is composed of 33 vertebrae that include 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5.

Human Back Pain Photograph by Sebastian Kaulitzki Fine Art America
Back muscles. The muscles of the back are a group of strong, paired muscles that lie on the posterior aspect of the trunk. They provide movements of the spine, stability to the trunk, as well as the coordination between the movements of the limbs and trunk. The back muscles are divided into two large groups: The extrinsic (superficial) back muscles, which lie most superficially on the back.
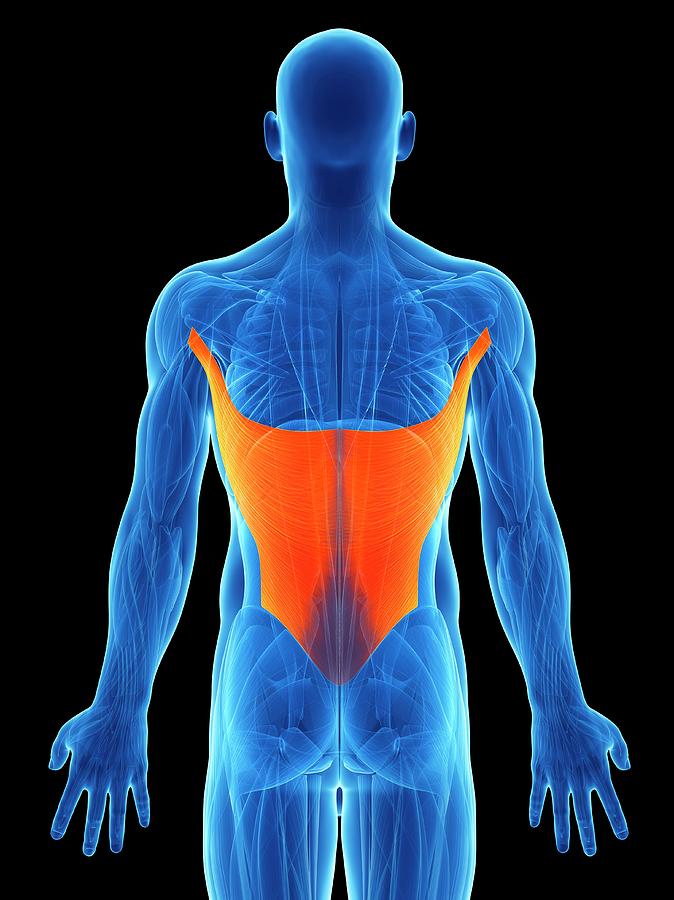
Human Back Muscles Photograph by Sebastian Kaulitzki
ABOUT About anatomy of the spine The human spine is a complex anatomic structure that is the scaffolding for the entire body. It provides several important functions, including: Protecting the spinal cord and nerves Structural support for the body, allowing us to stand upright. The spine supports about half the weight of the body.

Backbone Backache Science Anatomy Scan Of Stock Motion Graphics SBV
The muscles of your lower back and flexibility of your lumbar spine allow your trunk to move in all directions — front to back (flexion and extension), side to side (side bending) and full circle (rotation), as well as twist. The last two lumbar vertebrae allow for most of this movement. Protects your spinal cord and cauda equina.

Human Back Muscles, Realistic Drawing/illustration by nathan_jelbert
It protects the nervous system, facilitates movement, and enables communication between the brain and the rest of the body. Nevertheless, despite being such a critical structure in the human body, the spine is often misunderstood, which can lead to unnecessary fear and anxiety about spinal health.
Back Bones Diagram The bones of the lower back Stock Image F001
The human back, also called the dorsum ( pl.: dorsa ), is the large posterior area of the human body, rising from the top of the buttocks to the back of the neck. [1] It is the surface of the body opposite from the chest and the abdomen. The vertebral column runs the length of the back and creates a central area of recession.

Backbone Backache Science Anatomy Scan Of Stock Motion Graphics SBV
The spine, or backbone, is a bony structure that supports your body. It connects different parts of your musculoskeletal system, which includes your body's bones and muscles. Your spine helps you sit, stand, walk, twist and bend. Advertisement Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.